Enhancing Anastomotic Safety Through Pressure-Controlled Fixation
Colorectal and gastrointestinal surgeries often require stapling devices to reconnect tissues after resection. However, conventional staples can pose risks, especially when tissue thickness varies, leading to complications such as leaks, excessive trauma, and inconsistent healing.
The Challenge
Manual stapling tools offer limited control over compression levels and tissue adaptation. They often rely on operator experience, lack real-time feedback, and can result in poor fixation or damage to delicate tissue structures. These limitations increase the risk of postoperative complications, particularly in variable tissue environments.
The Solution
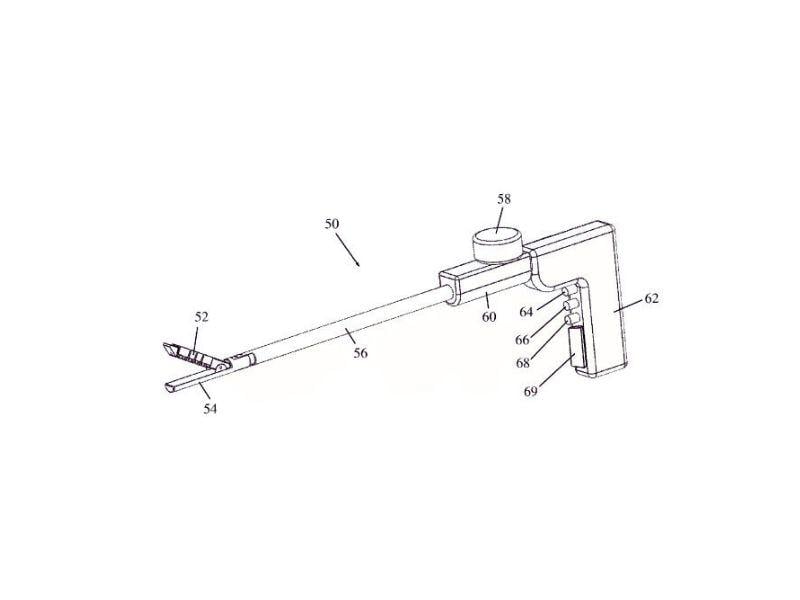
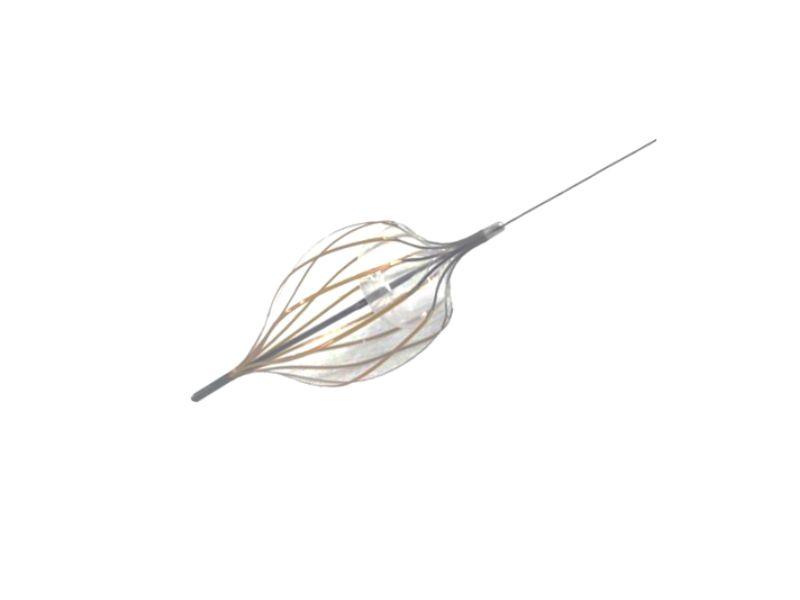
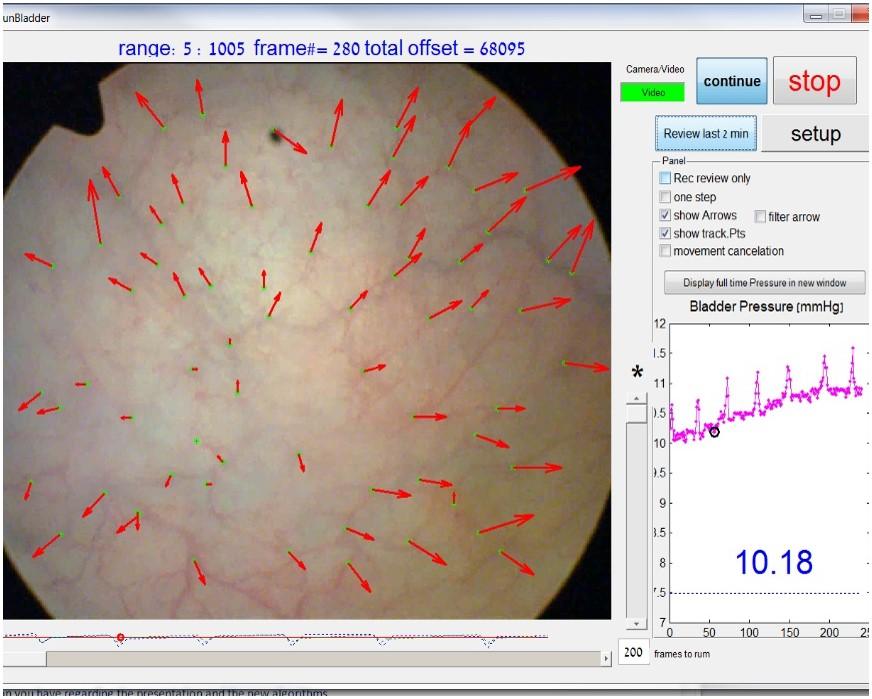
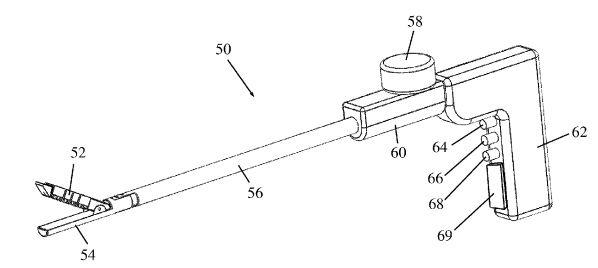
A novel stapling device that introduces real-time tissue pressure measurement and tack-like fasteners capable of adapting to different tissue thicknesses. The device ensures constant and controlled pressure across the anastomosis, minimizing trauma and improving healing outcomes. With over 45 degrees of articulation, it also allows better access in complex surgical settings.
- Tack-like fasteners maintain stable compression across variable tissue
- Integrated pressure sensing ensures optimal closure force
- Articulating head enables precise access and placement
- Prototype in production, with PCT filed and FDA 510(k) clearance expected in 2026
This next-generation system is designed to improve consistency, reduce complications, and set a new standard in surgical stapling for colorectal and GI procedures.